Manufactured wood, as the name suggests, is a type of wood that is manufactured rather than naturally sourced from a tree.
There are two basic types of commercially-used wood- solid wood and manufactured (engineered wood).
Solid wood, as you may already know, is what we call natural wood, i.e. the wood sourced from a tree.
It is engineered in a factory, generally by using parts of solid wood and other materials, including wood fibre, plastic, paper & more.
Also, it can be made to have even better qualities than natural wood. For instance, some high-grade plywoods can be even stronger and more durable than any solid wood. Moreover, engineered woods can be easily and widely produced with no threat to the environment and generally cost less than real wood.
Manufactured wood, these days, is used for practically every purpose, from furniture to different types of flooring and general construction.
Here’s an in-depth guide about different types of manufactured wood, including their purpose, uses, and various pros and cons.
What is Manufactured Wood?
A type of wood that is manufactured and not naturally sourced from a tree can be called manufactured wood.
It is generally made by combining different pieces of wood or different types of wood products together. Special ingredients including glue, chemicals, pressure & heat are used to provide extra strength and various qualities to engineered wood.
Based on the ingredients used and the method of construction, manufactured wood can be of many types, such as plywood, fiberboard, particleboard, etc.
Different Types of Manufactured Wood
There are many types of manufactured or engineered wood in use today. Different types of engineered woods are manufactured by using different wood products and joining materials in different quantities and under specific conditions. The most common types include:
1. Plywood
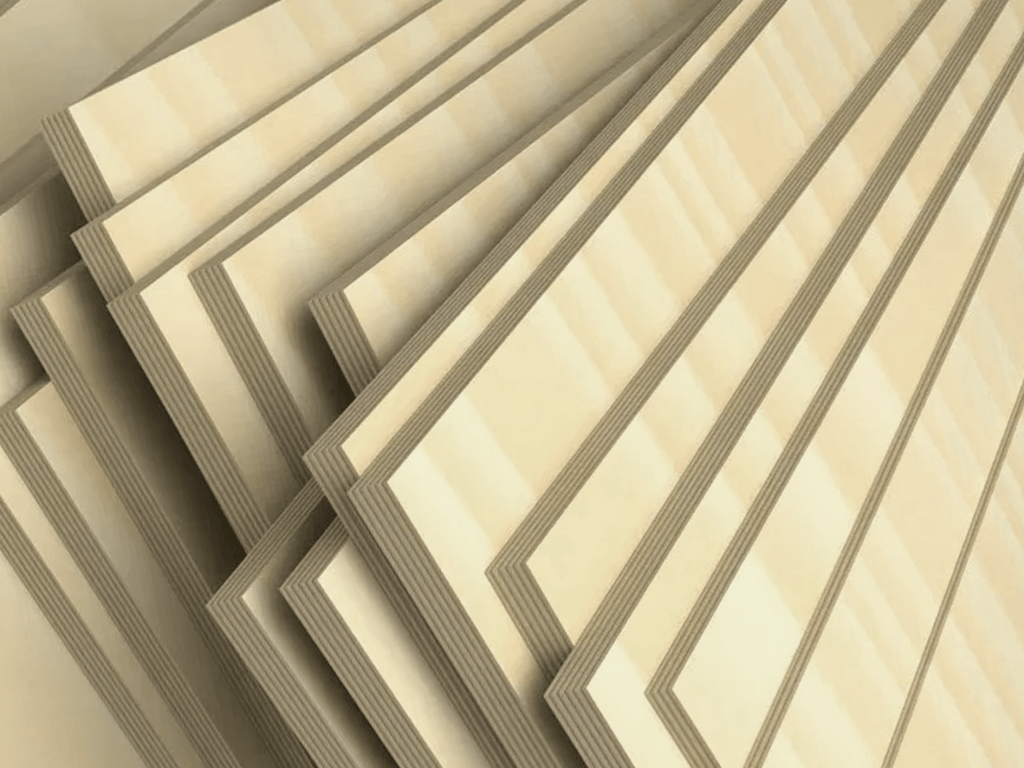
Plywood is one of the most common and popular types of engineered wood. It is also famous as the strongest manufactured wood.
Plywood is constructed by joining layers of veneers (also called plies) in a crosswire fashion using strong glue to form a solid and sturdy board.
Depending on the number and quality of veneer used, plywood can be classified into different grades – A, B, C, D, etc. – of which Grade A plywood is considered the best and can even be stronger and more durable than solid wood.
Uses of Plywood
Plywood is used for everything from flooring and furniture to the construction of structures, roofing, cabinetry, interior walls, partitions, wall sheathing & more.
Advantages
Looks goods. Has a top layer of natural wood, which makes it look similar to real wood. It is strong and durable and some species are also water resistant. They are treated to be resistant to termites and insect attacks. Plywood is easy to work with, glue, paint and polish.
Disadvantages
They are not naturally resistant to insects but can be treated easily. Plywood can easily peel off, i.e. layers can start coming off over years or due to constant wear and tear. It is one of the most expensive manufactured wood. Can be difficult to cut.
2. Particleboard or Chipboard

Particleboard is one of the cheapest, low-quality manufactured woods that is constructed by combining sawdust and resin using adhesives to form a solid board.
Particleboard or chipboard is often used in place of solid wood or plywood where quality is not a concern but the cost is. Because this type of wood costs less, it is commonly used in low-cost projects. Manufacturers often add layers of veneer on either side of a particleboard to make it look better and sturdier.
Uses
Common uses of particleboard include low-cost furniture, cabinets, wall panelling, partitions, flooring, false ceiling, underlayment, and doors.
Advantages
It costs less and is widely available. As a multitasking wood alternative, it makes a great choice for low-end furniture making. It is easy to work with and holds nails easily. It is lightweight and friendly to nature (renewable). It is also easy to paint and laminate. Maintenance is also easy.
Disadvantages
Particle boards are less durable than other types of manufactured wood. They are less dense, less strong and poorly resistant to water. Can be toxic due to the use of chemicals. Cannot bear heavy loads.
3. Fibreboard

Fibreboard is one of the strongest types of engineered wood. It is much denser than particleboard and is also resistant to wear and tear even after constant use.
Fibreboards are constructed by first boiling or steaming chopped wood pieces to turn them into wood fibres, which are then dried and bonded together using adhesives under specific temperature and pressure conditions to form strong manufactured wood boards.
Depending on the quality of the material and profess, fibreboards can be of the following types:
- MDF (medium-density fibreboard)
- LDF (low-density fibreboard)
- HDF (high-density fibreboard)
Uses
Fibreboards are used for general construction, soundproofing, insulation, furniture, cabinetry, doors, and home interiors.
Advantages
Fibreboard is strong, durable and easy to stain and paint. It is also inexpensive compared to plywood. It is lightweight and nature-friendly.
Disadvantages
Fibreboard is not resistant to moisture, not as strong as plywood, not easy to nail, and can take time to install.
- MDF
MDF is medium-density fibreboard. It is stronger than low-density fibreboard but less strong than HDF. It is suitable for outdoor applications because it can withstand changes in temperature and weather even better than real wood.
MDF is the most commonly used type of fibreboard and is often used as an alternative to solid wood.
- LDF
Low density fibreboard is the same as particle board or chipboard.
- HDF
High-density fibreboard is just like MDF, but stronger, harder and denser. It is also commonly called a hardboard.
4. Veneer

Veneer refers to a thin layer of solid wood that is obtained by peeling layers off a solid wood board or tree. It is most commonly used as a top layer on plywood, MDF and other manufactured woods to provide extra strength, protection and the appearance of natural wood.
Uses of Veneer
Veneering is used for flooring, furniture, walls, ceiling, and interior work.
Advantages
It is low cost, non-toxic, has high strength & durability, and looks great. Veneer is also used for making other manufactured woods.
Disadvantages
It is not water resistant and may require high maintenance.
5. Oriented strand board (OSB)
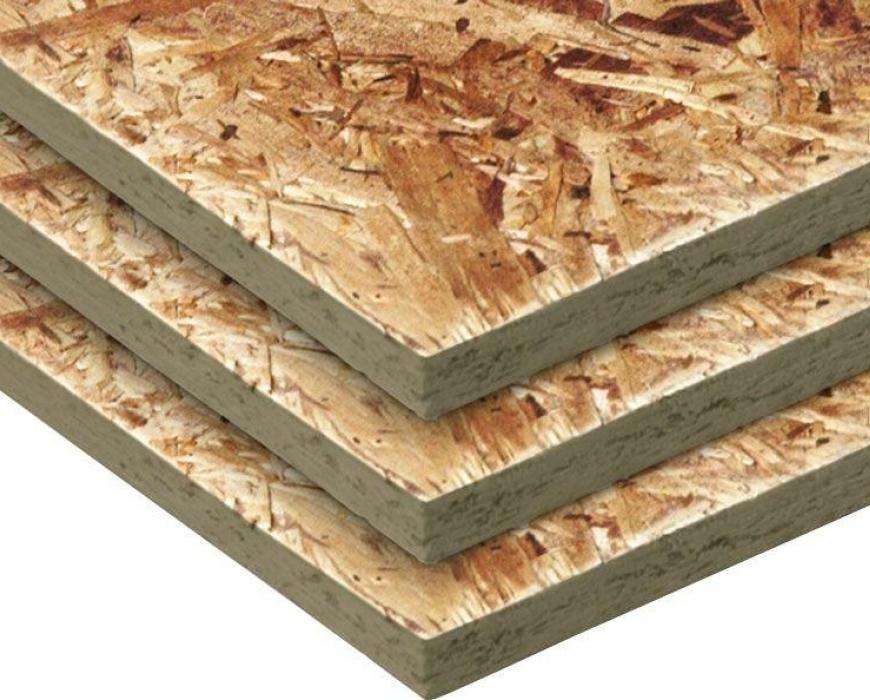

Oriented strand board (OSB) is a type of engineered wood panel made from strands of wood that are oriented in different directions & bonded together using resin and wax. The strands are usually made from small-diameter logs, wood waste or other wood materials that are mechanically shredded into thin strands.
Uses
Some common uses of Oriented Strand Board (OSB) include subflooring, furniture, packaging, and DIY projects. Its durability and affordability make it a popular choice in the construction, furniture, & packaging industries.
Advantages
It has several advantages that make it a popular choice in various industries. Firstly, it is more affordable than traditional plywood or solid wood. Secondly, OSB is durable & can withstand heavy loads and rough handling, making it ideal for construction, packaging, and furniture. Additionally, it is easy to work with and can be cut, shaped, and drilled using standard woodworking tools.
Disadvantages
OSB is more prone to swelling & warping than traditional plywood or solid wood. This can make it less suitable for use in humid or damp environments. Additionally, OSB is not as strong as plywood, which can limit its use in certain construction applications.
6. Blockboard

Blockboard is a type of plywood in which only the top and the bottom layers of a board are made of veneers while the interiors are made of blocks of solid wood. It is stiffer than plywood and doesn’t bend easily. It also cuts well and is overall easier to work with.
Uses
Blockboard is lightweight and easy to work with, making it a popular choice for DIY projects. It can be cut, drilled, and sanded to create various shapes and sizes. Blockboard is also available in a range of thicknesses and sizes to suit different applications, and can be finished with paints, stains, or varnishes to enhance its appearance. Overall, it is a versatile & cost-effective option for a variety of construction & furniture making projects.
Advantages
Blockboard has a smooth surface texture which makes it easy to finish with paints, stains, or varnishes. Moreover, It is available in a range of thicknesses and sizes to suit different applications, & can be more cost-effective than other materials such as solid wood.
Disadvantages
Blockboard may not be as strong as some other materials such as plywood, which can limit its use in certain construction applications. Additionally, it is not suitable for outdoor use or in areas with high humidity as it is prone to moisture.
Where to Buy Different Types of Manufactured Wood?
If you’re looking to buy manufactured wood, White Knight Consulting LTD is a reliable option. We supply a variety of manufactured wood types including MDF, particleboard, & plywood, among others. Our manufactured wood products are available to customers all around the world, including countries like Australia, Canada, Vietnam, Germany, UAE, South Africa, Turkey, & many more. We strive to provide high-quality manufactured wood that meets the needs of our customers. Whether you’re a construction company or a DIY enthusiast, White Knight Consulting LTD has the manufactured wood you need for your project.
